States That Don’t Tax Social Security
Seniors rely on Social Security and savings accounts during their transition to retirement. But when planning financially for retirement, people often overlook state taxes that will reduce their funds. To help, we identified each state that doesn’t tax Social Security as well as tax-friendly states for preserving retirement income.

- Written by Christian Simmons
Christian Simmons
Financial Writer
Christian Simmons is a writer for RetireGuide and a member of the Association for Financial Counseling & Planning Education (AFCPE®). He covers Medicare and important retirement topics. Christian is a former winner of a Florida Society of News Editors journalism contest and has written professionally since 2016.
Read More- Edited By
Lamia Chowdhury
Lamia Chowdhury
Financial Editor
Lamia Chowdhury is a financial content editor for RetireGuide and has over three years of marketing experience in the finance industry. She has written copy for both digital and print pieces ranging from blogs, radio scripts and search ads to billboards, brochures, mailers and more.
Read More- Published: January 5, 2023
- Updated: March 7, 2025
- 10 min read time
- This page features 15 Cited Research Articles
- Edited By
Social Security income amounts to approximately 30% of income for seniors, and an average of 66 million Americans receive the benefit each month. In certain states, however, you could face steep tax rates depending on your total income.
To help you plan for retirement, we’ve outlined every state that doesn’t tax Social Security below. Additionally, we’ve outlined tax-friendly states for retirees based on pension taxes, income taxes, cost of living and more.
States With No Social Security Tax
- Alabama: Retirement benefits are taxed as income, but pensions and Social Security benefits are exempt
- Alaska: No state income tax
- Arizona: Retirement benefits taxed as income, but Social Security is exempt
- Arkansas: Retirement benefits taxed as income, but Social Security is exempt
- California: Retirement benefits taxed partially, but Social Security is exempt
- Delaware: Retirement benefits taxed partially, but Social Security is exempt
- Florida: No state income tax
- Georgia: Retirement benefits taxed partially, but Social Security is exempt
- Hawaii: Retirement benefits taxed as income, but Social Security is exempt
- Idaho: Retirement benefits taxed as income, but Social Security is exempt
- Illinois: State income tax, but retirement accounts and Social Security are exempt
- Indiana: Retirement benefits taxed as income, but Social Security is exempt
- Iowa: Retirement benefits taxed partially, but Social Security is exempt
- Kansas: State income tax, but Social Security income is exempt
- Kentucky: Retirement benefits taxed partially, but Social Security is exempt
- Louisiana: Retirement benefits taxed partially, but Social Security is exempt
- Maine: Retirement benefits taxed partially, but Social Security is exempt
- Maryland: Retirement benefits taxed partially, but Social Security is exempt
- Massachusetts: Retirement benefits taxed as income, but Social Security is exempt
- Michigan: Retirement benefits taxed partially, but Social Security is exempt
- Mississippi: State income tax, but retirement accounts and Social Security are exempt
- Missouri: State income tax, but retirement accounts and Social Security are exempt
- Nebraska: State income tax, but Social Security income is exempt
- Nevada: No state income tax
- New Hampshire: State income tax, but retirement accounts and Social Security are exempt
- New Jersey: Retirement benefits taxed partially, but Social Security is exempt
- New York: Retirement benefits taxed partially, but Social Security is exempt
- North Carolina: Retirement benefits taxed as income, but Social Security is exempt
- North Dakota: Retirement benefits taxed as income, but Social Security is exempt
- Ohio: Retirement benefits taxed as income, but Social Security is exempt
- Oklahoma: Retirement benefits taxed partially, but Social Security is exempt
- Oregon: Retirement benefits taxed as income, but Social Security is exempt
- Pennsylvania: State income tax, but retirement accounts and Social Security are exempt
- South Carolina: Retirement benefits taxed partially, but Social Security is exempt
- South Dakota: No state income tax
- Tennessee: No state income tax
- Texas: No state income tax
- Virginia: Retirement benefits taxed partially, but Social Security is exempt
- Washington: No state income tax
- Washington, D.C.: Retirement benefits taxed as income, but Social Security is exempt
- Wisconsin: Retirement benefits taxed as income, but Social Security is exempt
- Wyoming: No state income tax
Some of these states, such as Alaska and Florida, have no income tax at all, meaning they don’t tax any form of retirement income including Social Security. Other states, such as Ohio and Indiana, have an income tax but choose to exempt Social Security.
While each above state won’t tax your Social Security benefits, it doesn’t mean you won’t be taxed at all. Your checks could still be taxed by the federal government if your individual income is greater than $25,000 or if you’re married with a joint income greater than $32,000.
15 Best States To Preserve Your Retirement Income
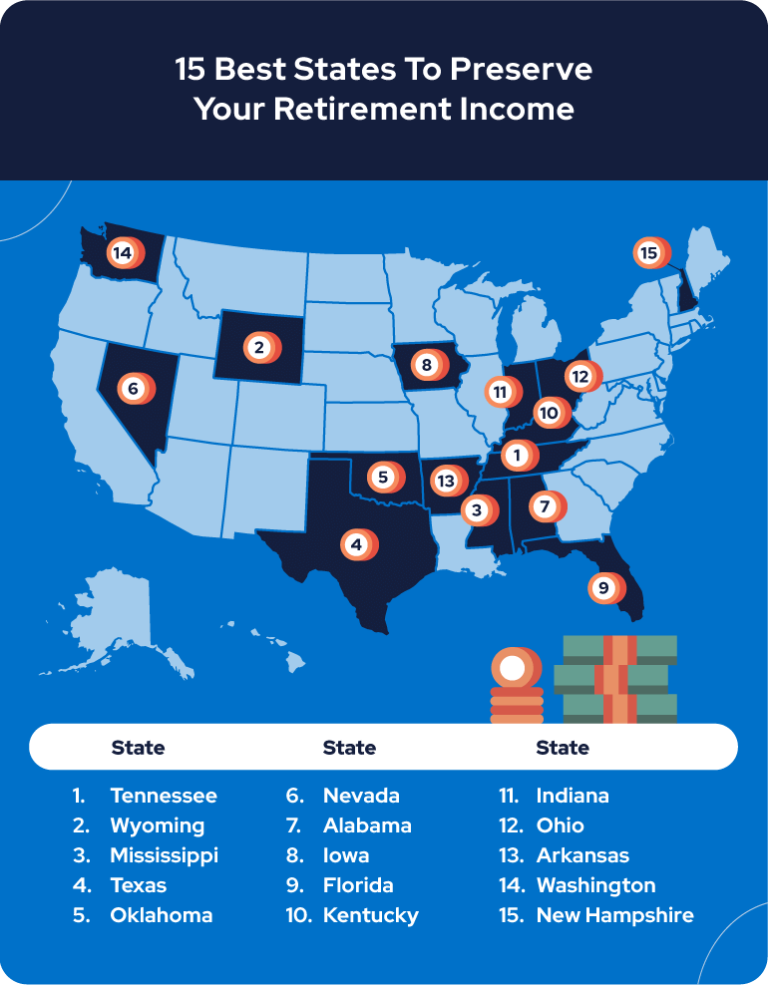
Social Security taxes are important to know, but it’s also important to take into account the cost of living and taxes on pensions, 401(k)s and military benefits. Considering these factors, we’ve created a list of the 15 most income-friendly states for retirees.
1. Tennessee
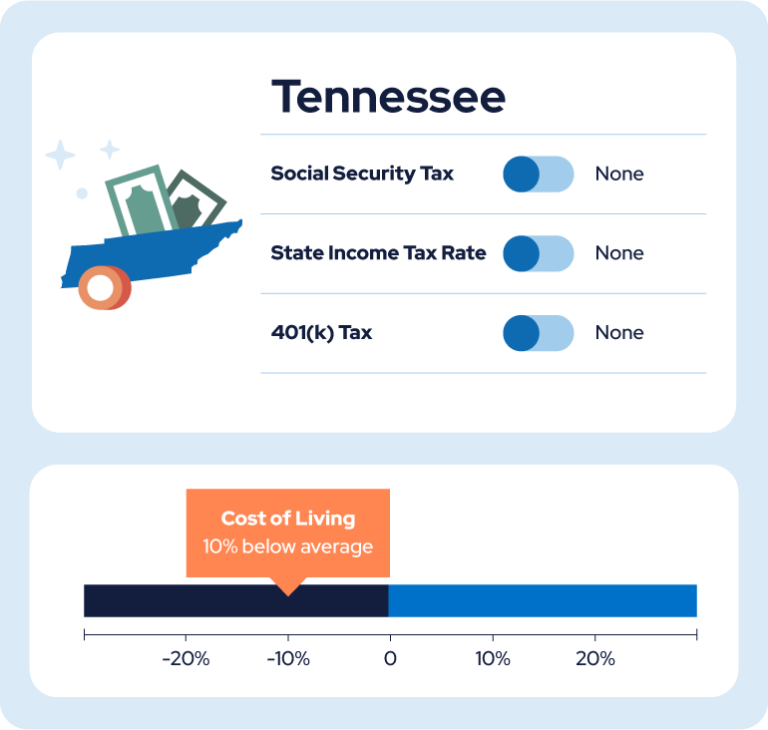
State income tax: No
Pension tax: No
401(k) tax: No
Military benefits tax: No
Income tax rate/range: N/A
Cost of living index: 90.4
Tennessee has no state income tax or taxes on other types of retirement income. It also has the sixth lowest cost of living, meaning it’s an ideal place to live and conserve your retirement funds.
2. Wyoming
State income tax: No
Pension tax: No
401(k) tax: No
Military benefits tax: No
Income tax rate/range: N/A
Cost of living index: 92.8
Wyoming doesn’t tax any form of retirement income and has a 10% lower cost of living than the national average. Eligible veterans may also receive a property tax exemption of $6,000.
3. Mississippi
State income tax: Yes
Pension tax: No
401(k) tax: No
Military benefits tax: No
Income tax rate/range: Mississippi has a flat 4.7% income tax rate.
Cost of living index: 85.3
Though Mississippi has a flat 4.7% state income tax, residents aren’t taxed for any types of retirement income. Since Mississippi also has the lowest cost of living of any state in the country, it’s one of the best places to save money during retirement.
4. Texas
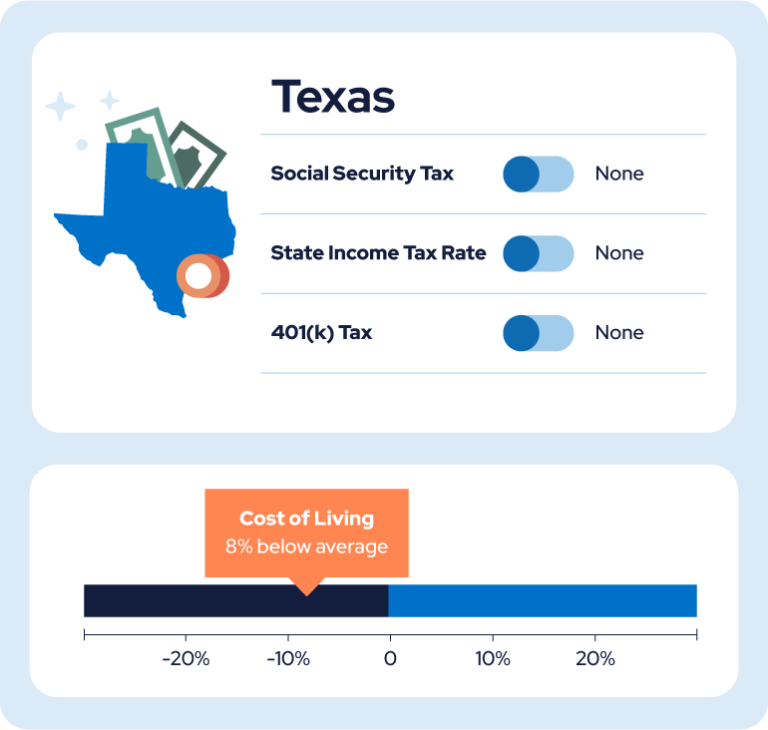
State income tax: No
Pension tax: No
401(k) tax: No
Military benefits tax: No
Income tax rate/range: N/A
Cost of living index: 93.0
Texas is another state that doesn’t levy income taxes, which means it doesn’t tax your pensions or other sources of retirement income. Additionally, veterans with a disability rating of 100% are exempt from all property taxes.
5. Oklahoma
State income tax: Yes
Pension tax: Yes
401(k) tax: Yes
Military benefits tax: No
Income tax rate/range: Oklahoma’s income tax ranges from 0.25% for those who earn between $0 and $1,000 annually to 4.75% for those who earn more than $7,200.
Cost of living index: 86.0
Oklahoma doesn’t tax Social Security, has a lower than average income tax rate and the second lowest cost of living in the U.S. Pensions, 401(k)s and IRAs are taxable, but taxpayers over 65 receive a deduction of $10,000 on income from retirement accounts.
6. Nevada
State income tax: No
Pension tax: No
401(k) tax: No
Military benefits tax: No
Income tax rate/range: N/A
Cost of living index: 101.3
Nevada has an average cost of living but distinguishes itself as a tax-friendly state for retirees since it has no state income tax. The Silver State also offers property tax exemption for veterans who served in the U.S. military during a wartime period.
*Ad: Clicking will take you to our partner Annuity.org.
7. Alabama
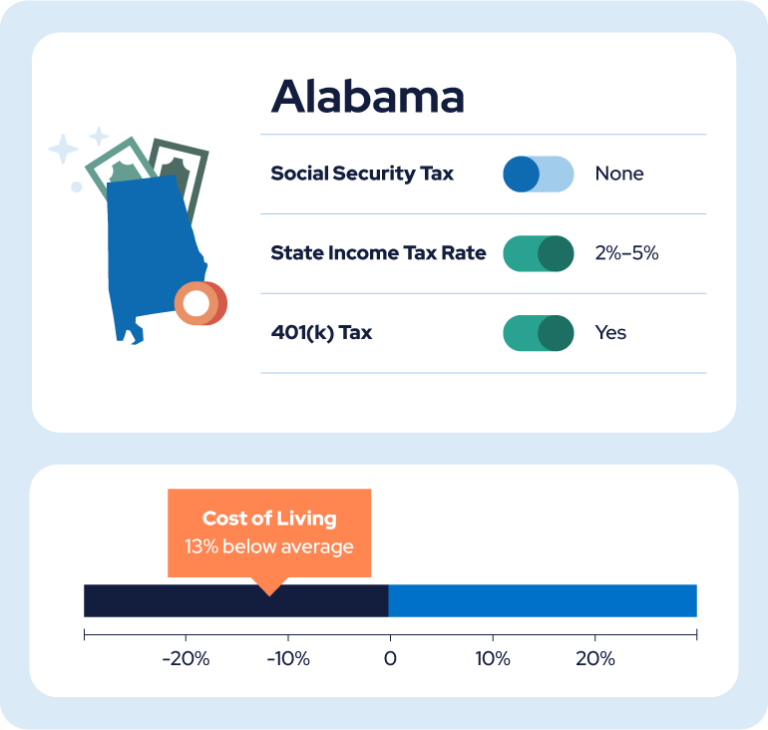
State income tax: Yes
Pension tax: None
401(k) tax: Yes
Military benefits tax: No
Income tax rate/range: Alabama’s income tax ranges from 2% for those who earn less than $500 annually to 4.75% for those earning more than $3,000.
Cost of living index: 88.8
While Alabama has an average income tax rate of 2% to 5%, it doesn’t tax pensions or military retirement benefits at all. It has the third lowest cost of living of any state, making it easier to conserve income in your golden years.
If you own property, you’ll also benefit from the homestead exemption, which decreases homeowner property taxes. If you’re planning to rely on income from a 401(k) or IRA, however, you’ll be taxed at the regular income tax rate.
8. Iowa
State income tax: Yes
Pension tax: Yes
401(k) tax: Yes
Military benefits tax: No
Income tax rate/range: For Iowa, income tax ranges from 4.40% to 5.70% depending on your income.
Cost of living index: 89.7
Iowa doesn’t tax military retirement income or Social Security. Income from 401(k)s, pensions and IRAs are taxed, but seniors can receive a deduction up to $6,000 if they file as single or $12,000 if they file jointly.
9. Florida
State income tax: No
Pension tax: No
401(k) tax: No
Military benefits tax: No
Income tax rate/range: N/A
Cost of living index: 102.3
Florida has no state income tax, meaning residents aren’t taxed for pensions, 401(k)s or any other type of retirement income. That said, the cost of living is more expensive than the average state.
10. Kentucky
State income tax: Yes
Pension tax: Yes
401(k) tax: Yes
Military benefits tax: No
Income tax rate/range: 4% flat rate
Cost of living index: 93.8
Social Security and military retirement income is exempt from taxation in Kentucky. While 401(k)s and IRAs are taxable, the Bluegrass State exempts retirement accounts with less than $31,110 from taxation. If your retirement income exceeds that amount, however, you’ll be taxed at the flat rate of 4%.
11. Indiana
State income tax: Yes
Pension tax: Yes
401(k) tax: Yes
Military benefits tax: No
Income tax rate/range: 3.05% flat rate
Cost of living index: 91.5
Indiana has an income tax rate on the lower side, at a flat rate of 3.05%. This and the state’s low cost of living helps seniors conserve funds during retirement. Military retirement pay is also exempt from income taxes.
12. Ohio
State income tax: Yes
Pension tax: Yes
401(k) tax: Yes
Military benefits tax: Yes (but deducted from income taxes)
Income tax rate/range: For Ohio, income tax ranges from 2.75% for those who earn $26,501-$100,000 to 3.50% for those earning more than $100,000.
Cost of living index: 94.0
Ohio doesn’t tax Social Security, but it taxes withdrawals from any retirement accounts as regular income. If your main source of income is an IRA or 401(k), this state won’t be very tax-friendly. However, the low cost of living will help offset funds lost from taxes.
13. Arkansas
State income tax: Yes
Pension tax: Yes
401(k) tax: Yes
Military benefits tax: No
Income tax rate/range: For Arkansas, income tax ranges from 0.0% for those who earn less than $5,300 annually to 3.9%. The state reserves lower tax brackets for people who earn less than or equal to $89,600 per year.
Cost of living index: 90.3
Arkansas has a cost of living 10% below average and has lower tax rates for people who earn less than $89,600 per year.
14. Washington
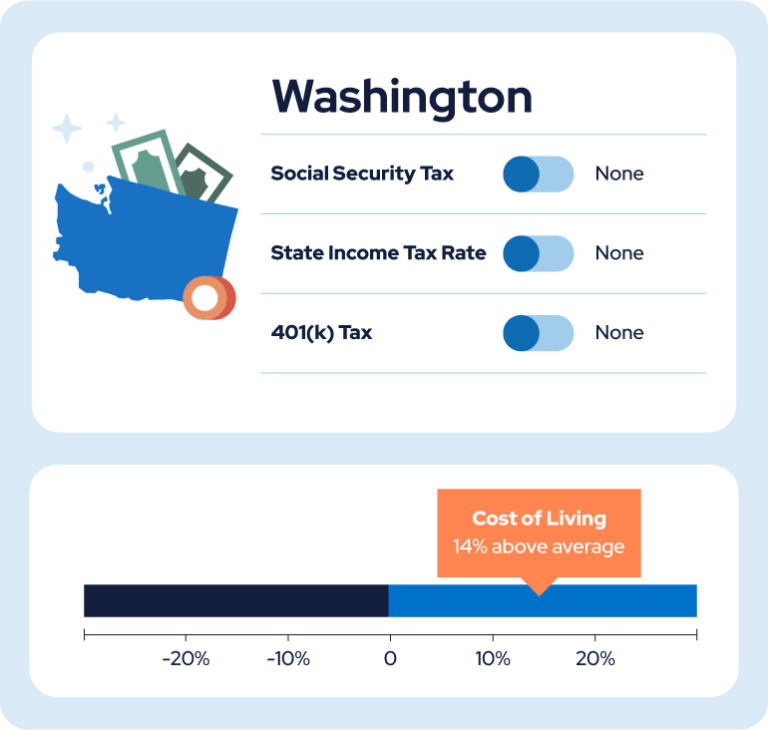
State income tax: No
Pension tax: No
401(k) tax: No
Military benefits tax: No
Income tax rate/range: N/A
Cost of living index: 115.1
As a Washington retiree, you are exempt from income taxes. However, the cost of living is 14% higher than the national average and its sales tax rate is one of the highest in the U.S. at 6.5%.
15. New Hampshire
State income tax: No
Pension tax: No
401(k) tax: No
Military benefits tax: No
Income tax rate/range: N/A
Cost of living index: 115.0
New Hampshire doesn’t have income tax, estate tax or sales tax, but has the third highest property taxes in the country, and cost of living is 14% higher than the average state. New Hampshire also taxes investment income above $2,400, but residents ages 65 and older can receive a $1,200 deductible.
Preparing for Retirement
Choosing the right location for retirement can have a major impact on your finances and overall quality of life. That’s why it’s important to know the tax policies and cost of living for the state where you retire.
If necessary, you might consider relocating to preserve your retirement income. For some moving tips for seniors, check out our infographic below.
Another important consideration when retiring is the cost of health care. To familiarize yourself with Medicare and how it can help you pay for health care, check out our full Medicare guide.
Expert Marc Guberti contributed to this article.
Connect With a Financial Advisor Instantly
Our free tool can help you find an advisor who serves your needs. Get matched with a financial advisor who fits your unique criteria. Once you’ve been matched, consult for free with no obligation.
15 Cited Research Articles
- Arkansas Department of Finance and Administration. (2020, December 22). Subject 206. Retrieved from
- https://www.dfa.arkansas.gov/images/uploads/incomeTaxOffice/206-PensionsAnnuities.pdf
- Iowa Department of Revenue (2022). Pension/Retirement Income Exclusion. Retrieved from https://tax.iowa.gov/expanded-instructions/pension-retirement-income-exclusion-2019
- Kentucky Department of Revenue. (2022). Individual Income Tax. Retrieved from https://revenue.ky.gov/Individual/Individual-Income-Tax/Pages/default.aspx
- Missouri Economic Research and Information Center. (2022). Cost of Living Data Series. Retrieved from https://meric.mo.gov/data/cost-living-data-series
- MyArmyBenefits. (2022). State/Territory Benefits. Retrieved from https://myarmybenefits.us.army.mil/Benefit-Library/State/territory-benefits
- New Hampshire Department of Revenue Administration. (2022, December 15). Frequently Asked Questions - Interest & Dividend Tax. Retrieved from
- https://www.revenue.nh.gov/faq/interest-dividend.htm
- Oklahoma Tax Commission. (2022). 2022 Oklahoma Resident Individual Income Tax Forms and Instructions. Retrieved from https://oklahoma.gov/content/dam/ok/en/tax/documents/forms/individuals/current/511-Pkt.pdf
- Social Security Administration. (2022). Frequently Asked Questions. Retrieved from https://faq.ssa.gov/en-us/Topic/article/KA-02471#:~:text=You%20must%20pay%20taxes%20on,income%E2%80%9D%20of%20more%20than%20%2432%2C000.
- Social Security Administration. (2022). Fact Sheet. Retrieved from https://www.ssa.gov/news/press/factsheets/basicfact-alt.pdf
- Travis County Tax Office. (N.D.). Property Tax Breaks, Disabled Veterans Exemptions. Retrieved from https://tax-office.traviscountytx.gov/properties/taxes/tax-breaks/disabled-vet-exempt#:~:text=In%20Texas%2C%20veterans%20with%20a,a%20%2410%2C000%20property%20tax%20exemption
- Tax Foundation. (2022). Tax Foundation by State. Retrieved from https://taxfoundation.org/center/state-tax-policy/
- Tax Foundation. (2022, October 25). 2023 State Business Tax Climate Index. Retrieved from https://taxfoundation.org/2023-state-business-tax-climate-index/
- Wyoming Department of Revenue. (2022). General Information. Retrieved from https://wyo-prop-div.wyo.gov/tax-relief
Your web browser is no longer supported by Microsoft. Update your browser for more security, speed and compatibility.
If you need help pricing and building your medicare plan, call us at 844-572-0696


